Hurricane Michael, other disasters can take lasting toll on children's mental health: Signs and solutions
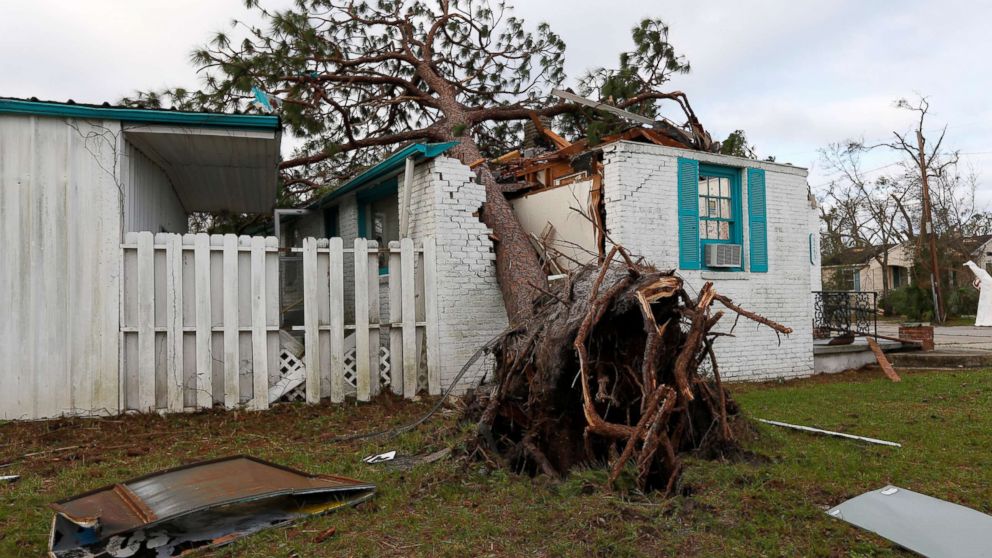
Windows boarded and emergency plans in place, with gallons of water and canned goods stocked. As people who are rushing to prepare for an impending natural disaster check items on to-do lists, it is possible to overlook a less visible need -- the mental health of children.
Stress reactions to calamities like hurricanes, floods and fires tend to show up in increased emergency room admissions, and such trauma can have a particularly lasting effect on children. Research shows that adverse childhood experiences today can turn into chronic illnesses in adulthood.
It's important to know that mental health problems are not uncommon in children. Ten to 20 percent of children and teens suffer from a diagnosable anxiety disorder. And it's highly likely many more suffer from anxiety issues that may not meet the criteria for a diagnosis, but still cause impairment and difficulty for the child. Since anxiety disorder is the most prevalent mental health condition in children, caregivers may want to help keep their child’s anxiety levels low during and after hurricanes and other disasters.
Here are some tips to understand how disasters may affect children's mental health and ways to help.
Why are children particularly vulnerable to trauma from disasters?
- Children are most vulnerable because they may not be able to understand all that is going on around them, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says.
- They may also struggle to communicate how they are feeling during this unfamiliar event that is threatening their safety and that of their family.
- Any child can suffer emotional distress from a disaster. But some children are at particular risk: Those who are under 8 years old and those who have endured trauma in the past or struggled with emotional, behavioral, or developmental problems.

What are some possible signs that a child is suffering mental stress after a calamity?
- They may show a change in their mood or behavior, such as becoming sad, anxious or scared, according to the CDC's blog, "Helping children cope with disaster."
- They may be more resistant to separating from caregivers to go to child care programs or school, or even to go to bed or play in another room.
- They may also have sleep problems -- sleeping too little or too much -- as well as headaches and stomachaches.
- Children often find it difficult to concentrate on school work after a disaster.
- Children may also, for a period of time, become more self-centered or immature and appear more clingy, less cooperative, more demanding, and irritable, the CDC says. Older children and adolescents may turn to smoking, alcohol, or other drugs to deal with their feelings.

How to help children weather a disaster with peace of mind?
- Inform children of what's going on with age-appropriate details, and start a conversation. Acknowledge it is a real-world problem, as opposed to fears from fairy tales or nightmares.
- Children need to know what they can expect and what you and other adults are doing to keep your family safe.
- Encourage them to ask questions.
- Teach children principles of deep breathing while they are calm. One possibility is to use a bottle of bubbles. Ask the children to focus on their breathing, take a deep breath allowing their tummy rise, and blowing the biggest bubble they can. This requires control so that the child will naturally breathe deeply with this activity.
- For children who already have anxiety, shielding them from their fears can work against them. A better approach is to offer nonjudgmental and validating phrases like, “I believe you can handle this!”
- Overexposure has the potential to inadvertently traumatize or re-traumatize children, so adults should limit what they say about the turmoil in front of kids and restrict exposure to media coverage of the disaster and its aftermath.
- Parents and caregivers may also want to ask friends and relatives for additional support for the family and children.
- Consider professional help such as from a therapist or psychologist if a child continues to be very upset for more than two to four weeks after the disaster; if their problems get worse instead of better over time; or if their reactions after their school work or relationships with friends or family.
- Stress may be unavoidable, but stress-related symptoms and disorders are preventable. It is possible to build resilience in children by remaining aware of the importance of healthy coping methods and the dangers of unchecked stress.
If you or a loved one needs help, there is a disaster distress helpline that operates every day at all times, run by the federal agency for mental health and substance abuse. Call 1-800-985-5990 or text TalkWithUs to 66746 to connect with a trained crisis counselor focused on distress from disasters.
Dr. Colette Poole-Boykin is a child psychiatry fellow at the Yale Child Studies Center and a member of the ABC News Medical Unit.